G-NIPT
Safe and Accurate Solution,
For Every Pregnant Woman and Baby

Powered by highly proprietary AI Technology,
G-NIPT delivers the best care solution for your little one.
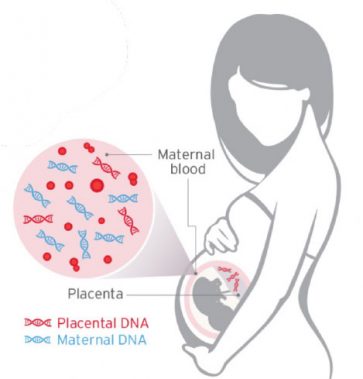
What is NIPT ?
NIPT is a screening test during pregnancy that detects certain genetic conditions in the fetus by analyzing the mother’s blood. It can be done after the 10th week of gestation and screens for major chromosomal abnormalities. It utilizes cell-free fetal DNA from the placenta, which increases in amount as the gestational age progresses.
NIPT screens for major chromosomal aneuploidies like Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and Patau syndrome. While NIPT provides high accuracy, it is a screening test, not a diagnostic test. If higher risk is indicated, additional diagnostic testing such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling may be recommended for confirmation.
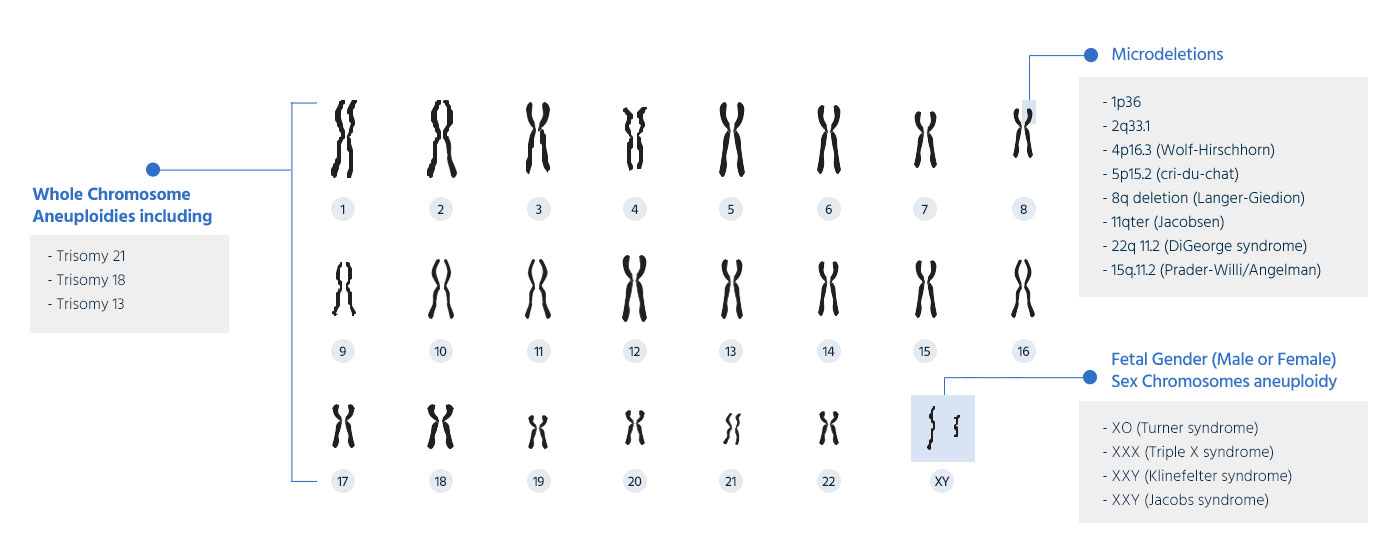
What does G-NIPT screen for?
Genome-wide scanning method: Screens all 23 chromosomes and reports major microdeletion syndromes with high clinical significance.
In the case of twins, the sex chromosome aneuploidy is not reported. The result will tell you the female twin case and whether the Y chromosome is detected or not and cannot determine if one or two of the fetuses are male.

How is it different from other screening and diagnostic tests?

Safer than the invasive amniotic fluid test
Accurate than other screening options


Accurate than other screening options

| Other Prenatal Screening for chromosomal abnormalities | G-NIPT | Confirmatory Diagnostic Tests | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Screening | Screening | Diagnostic |
| Sensitivity | 80~97% | 99% | 99% |
| False-positive rate | ~5% | Below 1% | Below 1% |
| Risk of miscarriage | Almost none | Almost none | Exists |
| Testing timing | After 11weeks | At 10~22 weeks | At 15~20 weeks |
| Testing method | Biochemical marker test | NGS method | Karyotyping |
* The information above is based on Down Syndrome.
1) Raw Obstet Gynecol, 2013; 6(2); 48-62. 2) Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2015 Aug; 213(2); 214
Who should consider having G-NIPT?
NIPT is ESSENTIAL for mothers who meet ANY of below criteria.
『
NIPT is recommended regardless of Age or Risk factors
』
How does NIPT work?
Clear answers in just three simple steps.
Test Performance
- Analysis of over 57,000 NIPT cases for G-NIPT performance evaluation
- G-NIPT has proven the accuracy of the test through the analysis of multiple clinical samples and it provides reliable results.
| Sensitivity | Specificity | NPV | PPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 21 | 99.73% | 99.99% | >99.99% | 98.92% |
| Trisomy 18 | 99.22% | 99.98% | >99.99% | 95.49% |
| Trisomy 13 | >99.99% | 99.99% | >99.99% | 87.50% |
| Sex chromosome aneuploidy (XO,XXX,XXY) |
>99.99% | 99.86% | >99.99% | 48.65% |
| Other Chromosomes | The clinical sensitivity was not determined due to low incidence. | |||
| Microdeletion Syndrome | The Clinical sensitivity was not determined due to low incidence, and the sensitivity may be significantly affected by factors such as fetal DNA fraction and microdeletion size | |||
* Test performance is based on the G-NIPT test result conducted between 2015.12~2022.10 and may be changed in the future.
Disease Information
Powered by highly proprietary AI Technology,
G-NIPT delivers the best care solution for your little one.
What does G-NIPT screen for?
Copy Number Variation Reporting
- Reporting CNVs(deletion/duplication) which size is more than 7Mb.
- Reporting deletion/duplication showing “Sufficient evidence for pathogenicity” in the ClinGenDB curated by the Clinical Genome Resource(ClinGen) in the US.
- The sex chromosome aneuploidy is not reported in the case of twins.
- In the case of twins, the result will tell you the female twin case and whether the Y chromosome is detected or not and cannot determine if one or two of the fetuses are male.
Why G-NIPT for your patients ?
G-NIPT is validated with > 99.4% accuracy and 99.07% sensitivity 1
- In this study, we developed a novel NIPT method using cfDNA fragment distance (FD) and convolutional neural network-based artificial intelligence algorithm (aiD-NIPT).
- In an analysis of 17,678 clinical samples, all algorithms showed >99.40% accuracy for T21/T18/T13.
Test Performance
- Analysis of over 57,000 NIPT cases for G-NIPT performance evaluation
- G-NIPT has proven the accuracy of the test through the analysis of multiple clinical samples and it provides reliable results.
| Sensitivity | Specificity | NPV | PPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 21 | 99.73% | 99.99% | >99.99% | 98.92% |
| Trisomy 18 | 99.22% | 99.98% | >99.99% | 95.49% |
| Trisomy 13 | >99.99% | 99.99% | >99.99% | 87.50% |
| Sex chromosome aneuploidy (XO,XXX,XXY) |
>99.99% | 99.86% | >99.99% | 48.65% |
| Other Chromosomes | The clinical sensitivity was not determined due to low incidence. | |||
| Microdeletion Syndrome | The Clinical sensitivity was not determined due to low incidence, and the sensitivity may be significantly affected by factors such as fetal DNA fraction and microdeletion size. | |||
* Test performance is based on the G-NIPT test result conducted between 2015.12~2022.10 and may be changed in the future.




