i-screen
(Newborn Genome Screening)
The faster you know,
The more accurate you know.

“Is it all you see in your baby?“
i-screen empowers parents with valuable insights into their babies’ genetic health and intervention for potentially inherited conditions.
What is i-screen ?
Newborn Genome Screening is a comprehensive genetic test performed shortly after birth to evaluate a baby’s DNA for potential genetic disorders. It involves analyzing the entire genome and providing valuable information about your baby’s risk for various inherited conditions.
i-screen can help identify conditions that may not be apparent at birth, allowing for early intervention and personalized medical management. By detecting genetic disorders early, parents can make informed decisions about their child’s healthcare and potentially improve long-term outcomes.
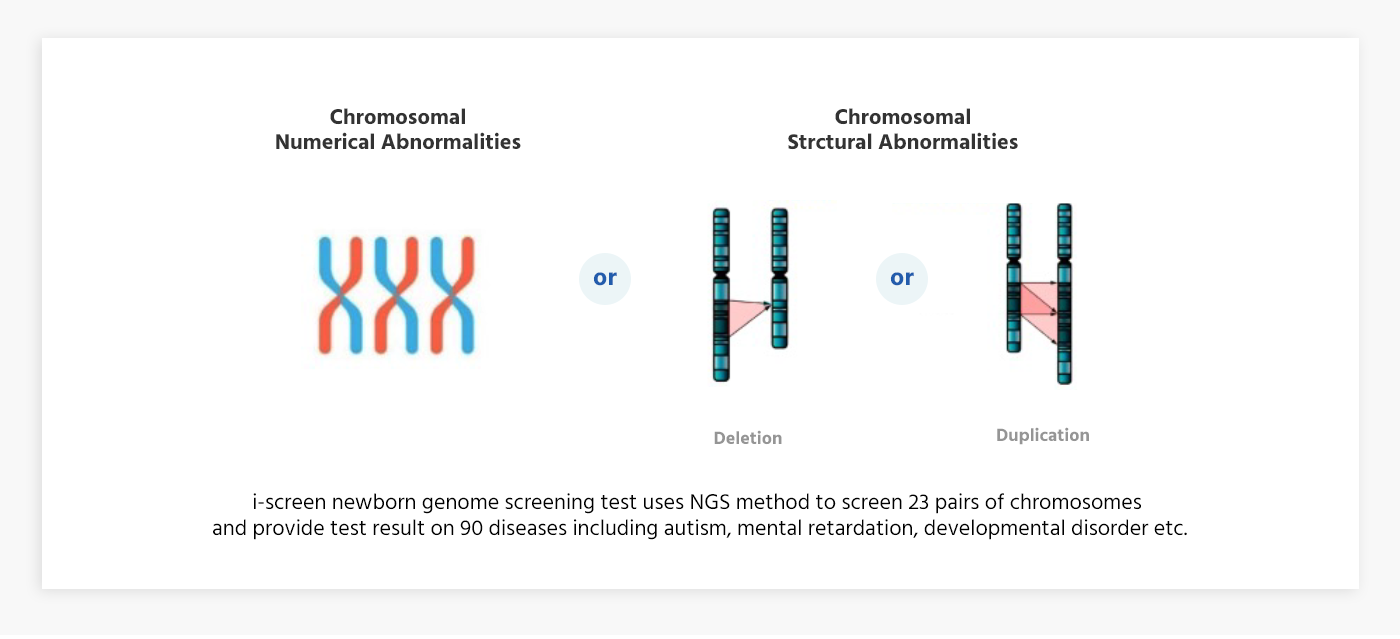
What does i-screen for?
check for chromosomal Numerical & abnormalities in newborns
Why do Genomic Disorders Occur ?
Genomic disorders can occur to anyone during the fertilization and cell division processes of the pregnancy. In most cases, genomic disorders do not have a hereditary nature. The risk of occurrence is the same in every pregnancy regardless of family history. Few diseases occur naturally with older maternal age.
How does i-screen work?
How is it different from CMA* test?
| Category | i-screen | Chromosomal Micriarray(CMA) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Chromosome disease screening | Chromosomal disease diagnosis | |
| Method | Targeted DNA CNV(NGS) | Chip-based array CNV | |
| TAT | 6days | 10days | |
| Detection rate | 10~15% | 15~20% | |
| Markers | CNV SNP |
Not applicable Not applicable |
550,000 220,436 |
| Types of chromosomal abnormalities |
Deletion | >400kb | >400kb |
| Gain | >400kb | >400kb | |
| UPD | – | O | |
| Monosomy/ Trisomy |
O | O | |
| Trisomy | O | O | |
| Unbalanced translocation | X | O | |
| Balanced translocation | – | – | |
| mosaicism | – | △
(According to the number of cells) |
|
| homozygosity | – | O | |
| inversion | – | – | |
| Loss Of Heterozygosity (LOH) |
– | >5Mb | |
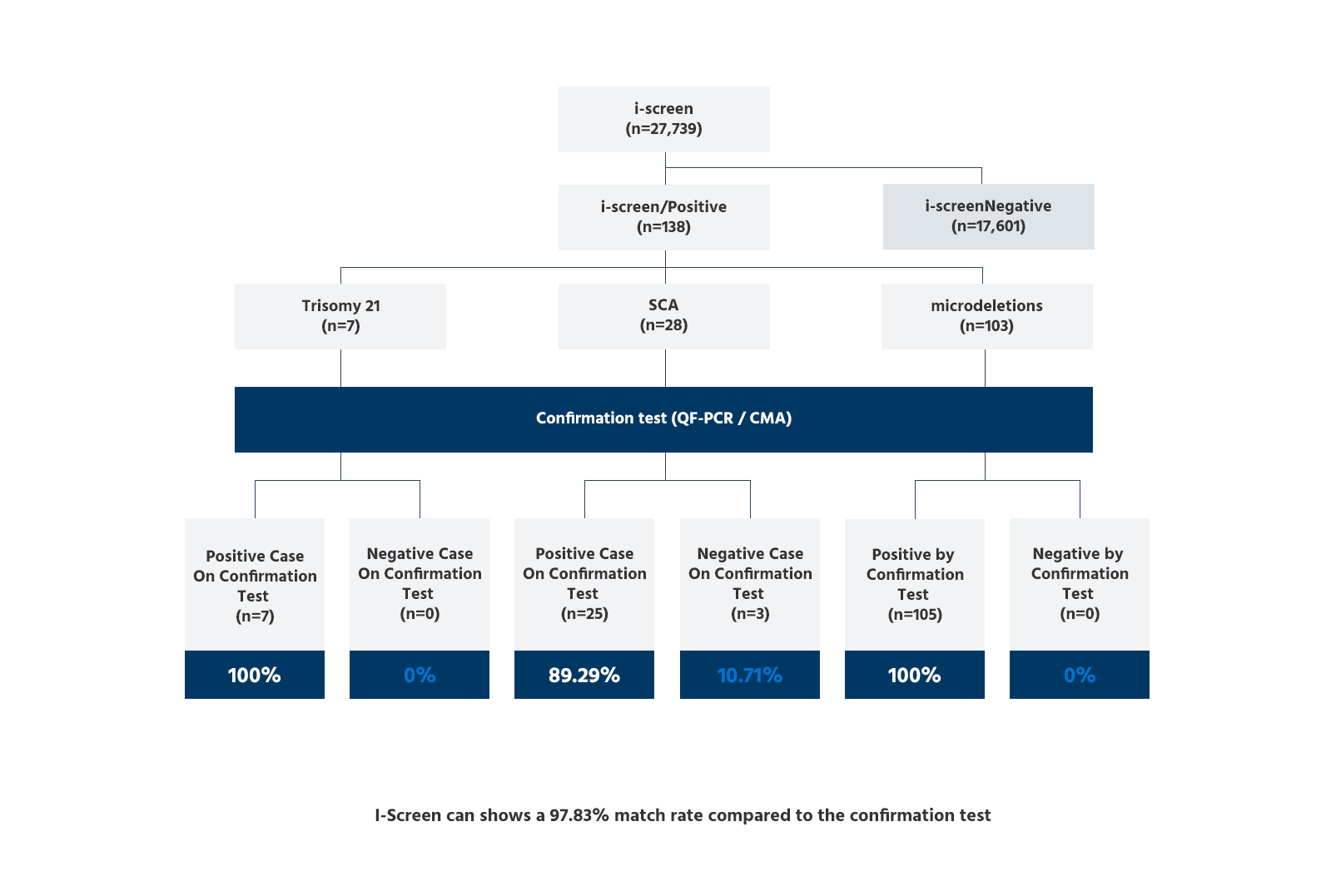
i-screen can show a [97.83%] match rate compared to the confirmation test.
Who should consider having i-screen?
Genomic disorders can occur to anyone during the fertilization and cell division processes of the pregnancy.
In most cases, genomic disorders do not have a hereditary nature. The risk of occurrence is the same in each pregnancy regardless of family history. Few diseases occur naturally with older maternal age.
How does it works?
Clear answers in just three simple steps.
Disease
i-screen is a vital tool for you to identify potential genetic disorders and develop personalized treatment plans for newborns.
What regions of the chromosome is covered?
To screen for 90+a Diseases, 170,000 different regions of chromosome are analyzed.
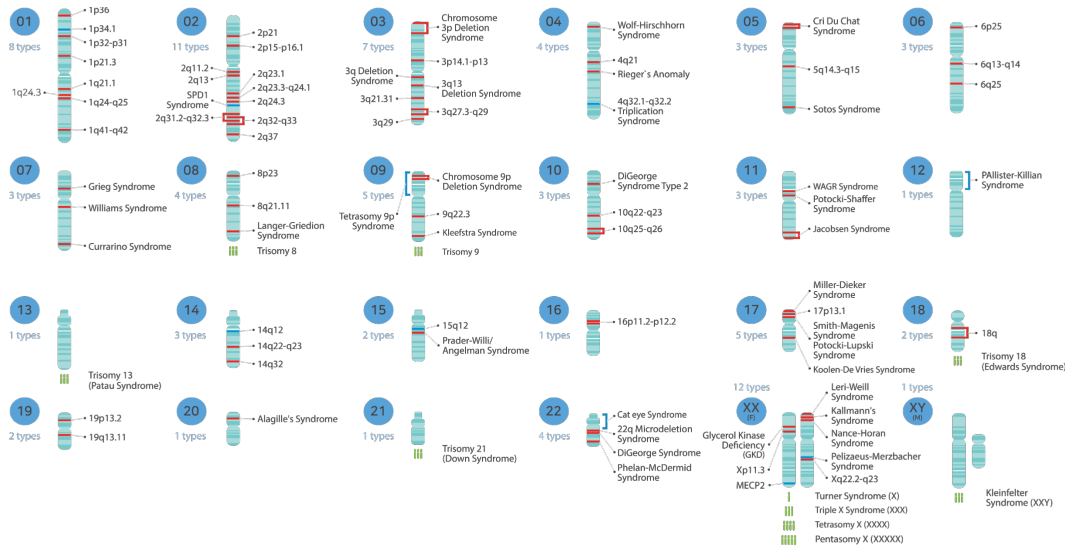
- Diseases were selected based on the list of developmental disorders related to chromosomal abnormalities discovered until recently.
- Selected mainly for diseases that have a high incidence and can lead to relieved symptoms through early detection and treatment.
LIMITATIONS
- This test is a screening test for rare diseases associated with developmental disorder such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome,
and Patau syndrome. If the result is positive, confirmatory tests such as karyotype analysis, FISH, microarray, etc., are needed for accurate diagnostics. - Genetic variants(balanced trans location, inversion, point mutation, low-level mosaicism, etc.)other than chromosomal deletion or duplication are not detected.
- It is difficult to rule out the possibility that the disease was caused by chromosomal abnormalities that could not be detected.
- Chromosomal deletion/duplication that has unclear clinical significance in medical level at the point of reporting is not reported.
- This test is conducted with the consent of the patient and does not directly aim at the treatment of disease or injury.
Why i-screen for your patients ?
Test Performance
i-screen VS CMA (confirmation test)
Disease